Article Courtesy by Paola Ochoa, AgTools
The first consumption of onion dates to more than 5,000 years ago, in the Middle Ages. It was so highly valued that it functioned as a means of payment and was given as a gift to show appreciation or thanks. And beyond providing food, the onion was given a great use in medicinal treatments, as it acts as a natural diuretic, and is used against heart, eye, and joint diseases, so it is not surprising that we find the onion as a key ingredient in more than one home remedy of grandma’s recipe book.
The onion is a basic ingredient in recipes from all regions; it is the only truly global ingredient, providing flavor and texture to food.
In Latin America, you cannot imagine delicious guacamole, a good torta, or a taco without chopped onion, plus it can be eaten raw, cooked, or fried, and the possibilities are endless. In addition, it is a source of fiber, and this fiber is soluble, which can reduce the probability of developing cardiovascular diseases.
Related Article: International Fresh Produce Association’s The Mexico Conference Returns in Person
One of the incredible properties of onion is that it is known as the vegetable insulin thanks to the fact that it contains glucoquinine, which is incredibly beneficial against diabetes by acting as a controller of sugar levels.
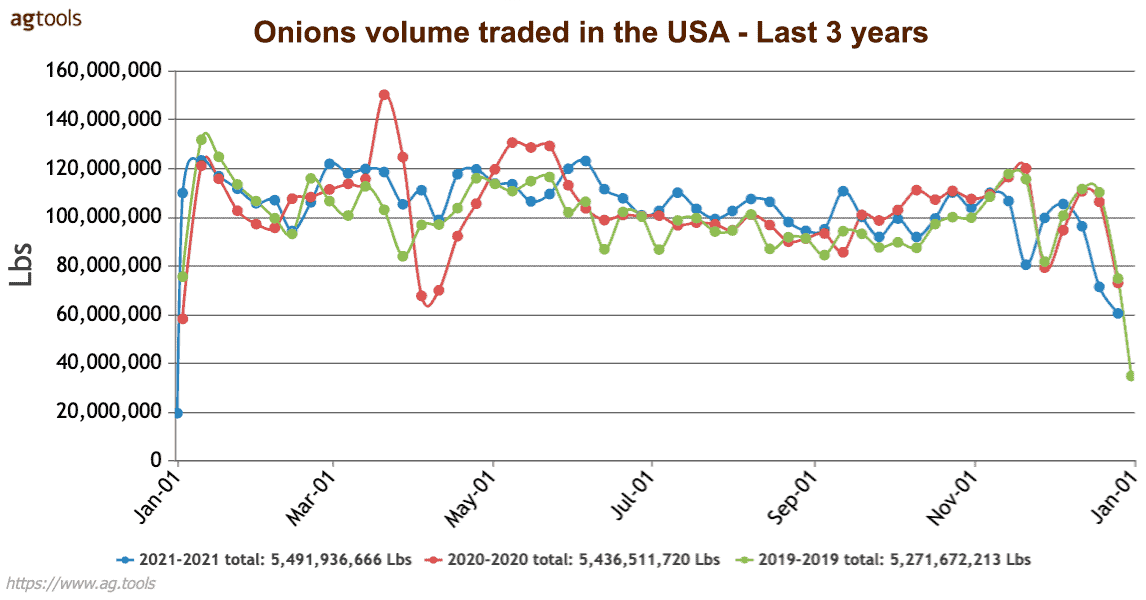
In 2019 in the United States, 5.2 billion pounds of onions were marketed, while in the year 2021 there was marketing of 5.4 billion pounds, which represents an increase of 3.84%, which we can appreciate in the following graph:
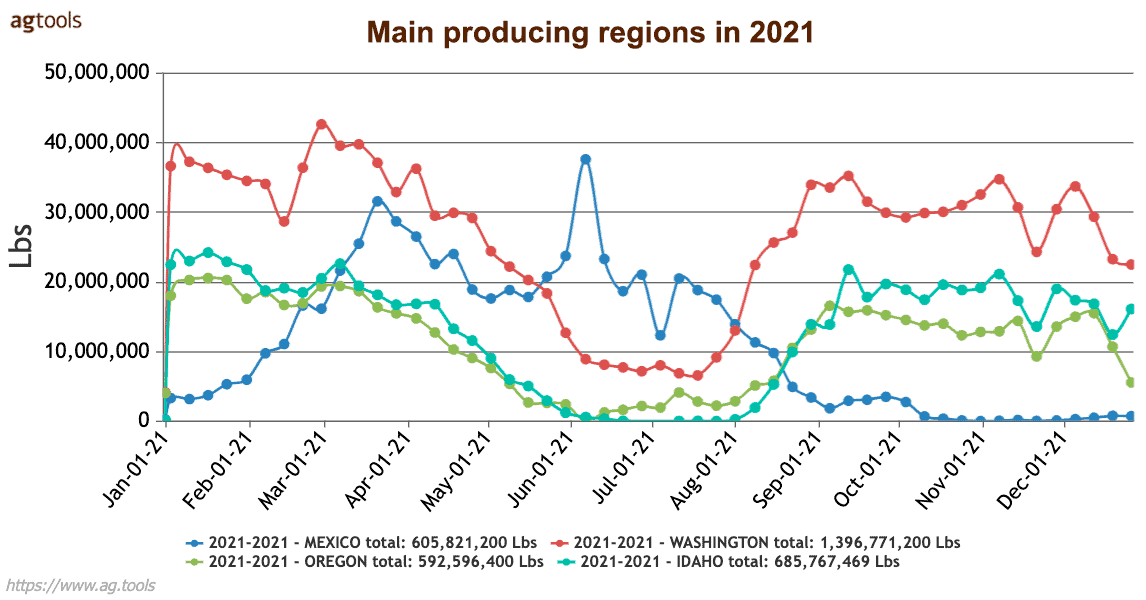
59.74% of these onions come from four main regions:
- Washington, with 25% of production, with Columbia Basin being the region with the largest production.
- Idaho, with 12%, mainly in the eastern region of the state.
- Mexico, with 11%.
- Oregon with 10%.
These regions complement each other to produce year-round, making it possible to cook onions all 12 months of the year.
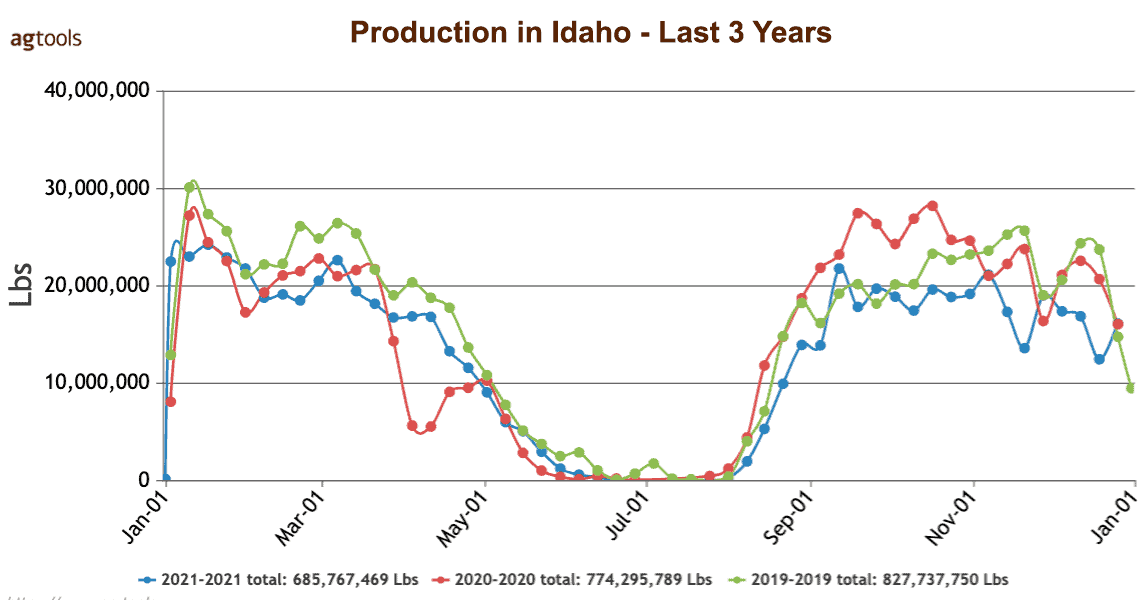
Idaho, which is the second-largest onion producer in the United States, has had a decrease in production volumes of 17% compared to 2019. Over the past three years, this decrease has been seen over the past three years, reaching its lowest production level in the past five years in 2021.
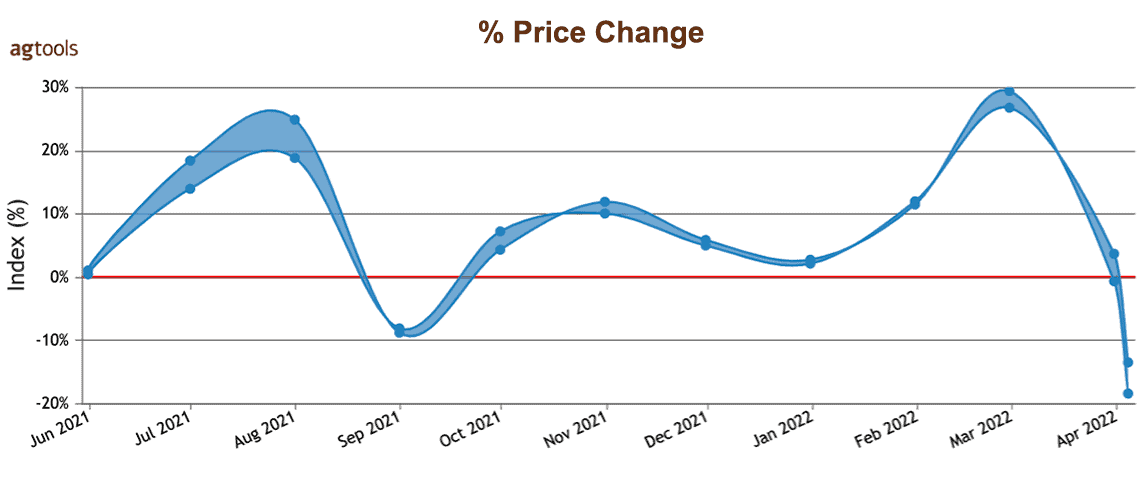
These adjustments in the volume of onion production have caused some months its price to be very volatile and change a lot from one month to another and are that the demand for this vegetable continues to increase more and more, as we can see in the following graph.
So, it seems that the onion has only one value that is not pleasant, that of provoking a few tears when cut. This also has an explanation! The water or oil of the onion contains sulfur and is what causes irritation when cutting it, so we can say that it is rich in minerals (calcium, magnesium, sulfur) among others, and contains vitamins (A, B, C, and E).